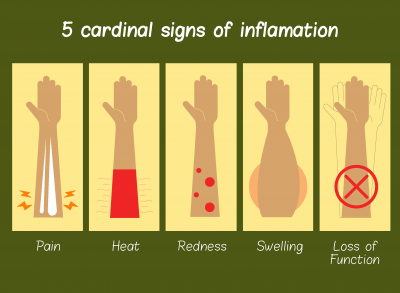
Chronic Inflammation- Cascading Chain of Reactions
Inflammation is a matter of life and death; it is our body’s necessary response to our internal defense system. However, when inflammation becomes self-perpetuating, it can lead to chronic inflammation, which can last for months or years and requires medical intervention to prevent further inflammation-mediated damage and trauma.
Chronic inflammation is inflammation of prolonged duration, involving active and sustained inflammation, healing, and tissue injury simultaneously.
So, what triggers this self-limiting form of inflammation turn to dysregulated chronic inflammation?
Triggers:
- Persistent infections: Failure to eliminate agents causing acute inflammation like bacteria, fungi, parasites, and protozoa.
- Physical injuries: Severe injuries like musculoskeletal injuries cause lifelong health problems as they cause prolonged inflammation in the damaged tissues.
- Allergies and food sensitivities: Allergens like pollen, mold, dust, and food sensitivities (with reactions similar to that of allergies) can raise levels of immunoglobulin E (IgE) adding to prolonged inflammation. Irritants and foreign materials also add to inflammation.
- Age-related wear and tear: Age-related tissue breakdown, with the immune system’s response to it, along with a pro-inflammatory diet.
- Dietary deficiencies and imbalances: Eating too many calories or carbs, imbalance of fats, excess sugars generates C-reactive protein and other inflammatory substances.
- Environmental stresses: Common environmental stresses like tobacco smoke, cold air (for asthmatic patients), and other triggers can stimulate chronic inflammation by increasing free radicals.
Impact of Chronic Inflammation on Body
Chronic inflammation is the core of “-itis” diseases, further associated with various auto-immune diseases, metabolic syndrome, neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, and vascular diseases. Here are some of the harmful effects of chronic inflammation on the human body:
- Brain: Inflammation in the brain causes swelling of brain tissue or blood vessels, resulting in various deficits like stroke, memory or vision loss, speech impairment, confusion, etc.
- Skin: Chronic inflammation can lead to inflammatory skin disorders like dermatitis, blistering disorders, photosensitivity reactions, etc.
- Heart: Inflammation of heart muscles or myocardium can cause three main types of heart inflammation like endocarditis, pericarditis, and myocarditis.
- Liver: Liver inflammation or hepatitis is usually caused by a viral infection or auto-immune disease, with symptoms like abdominal swelling, water retention, loss of appetite to other serious conditions.
- Kidney: Kidney inflammation or nephritis can cause symptoms like swelling of body parts, fever, burning sensation/pain while urinating.
- Bones: Chronic inflammation leads to more fractures and conditions like osteoporosis.
- Muscles: Prolonged muscle inflammation can lead to slow yet progressive muscle weakness and wasting, muscle fatigue, difficulty breathing or swallowing, discoloration, etc.
- Lungs: Chronic inflammation of lungs show symptoms like pain on one side of the chest, shallow or painful breathing, headaches, etc.
- Thyroid: Inflammation of thyroid (thyroiditis) leads to fatigue, unexplained weight gain, dry skin, irritability, etc.
- GI Tract: Inflammation of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract results in damage to the stomach lining, with complications like IBS, celiac disease, GERD, etc.
Key Takeaway






Leave A Comment